Democratizing Data: Making Insights Accessible to All
Democratizing Data: Making Insights Accessible to All
In today’s digital age, data has become more than just a buzzword—it’s a critical asset that fuels innovation, drives decision-making, and shapes strategies across industries. However, the true power of data lies not just in its accumulation but in its accessibility and usability by everyone within an organization. This concept, known as democratizing data, is transforming how businesses operate, empowering employees at all levels to leverage data-driven insights to drive success.
Understanding Democratizing Data
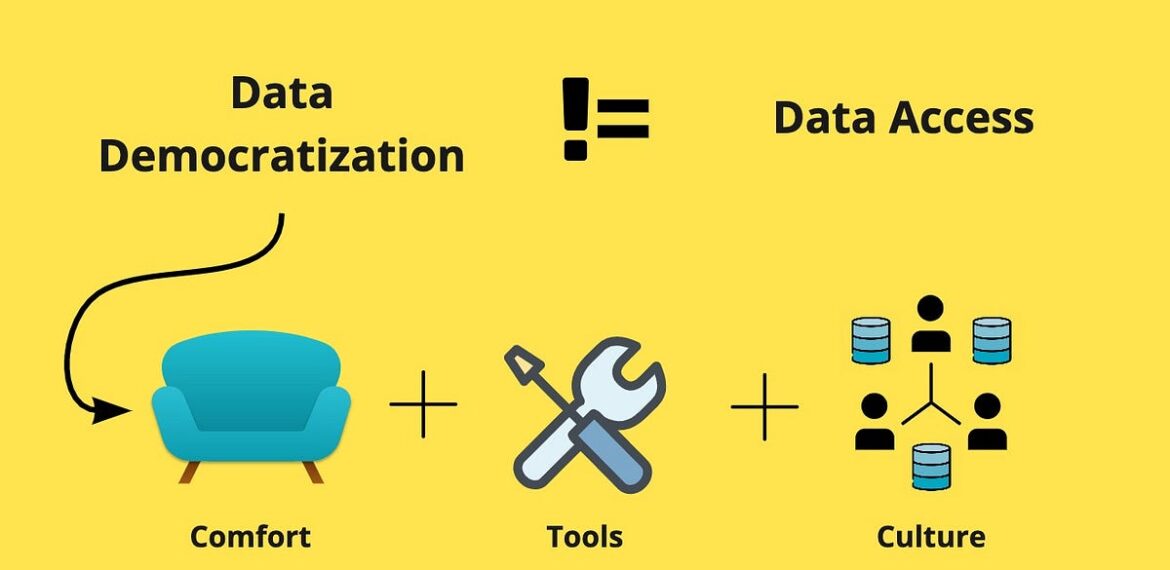
Democratizing data refers to the process of making data and insights accessible to a broader audience within an organization, beyond traditional data experts and analysts. Historically, data has been siloed within specific departments or centralized teams, creating barriers to access for those who need it most—managers, frontline employees, and decision-makers across various functions. Democratizing data aims to break down these barriers, enabling anyone within an organization to access, interpret, and use data effectively to inform decisions and drive innovation.
The Importance of Democratizing Data
1. Fostering Informed Decision-Making:
Democratizing data empowers individuals across all levels of an organization to make informed decisions based on accurate insights rather than intuition or incomplete information. Whether it’s a marketing manager analyzing campaign performance, a product manager identifying customer preferences, or a sales executive forecasting market trends, democratized data ensures that decisions are grounded in data-driven evidence, leading to better outcomes and mitigating risks.
2. Driving Innovation:
Innovation thrives on access to information and diverse perspectives. By democratizing data, organizations foster a culture where employees are encouraged to explore and experiment with data to uncover new opportunities, improve processes, and develop innovative solutions. When employees have the tools and resources to analyze data independently, they can contribute meaningfully to driving continuous improvement and competitive advantage.
3. Enhancing Transparency and Accountability:
Access to data promotes transparency within an organization. When insights are readily available to all stakeholders, decisions become more transparent, fostering trust and accountability. Transparency in data usage and decision-making processes not only improves internal collaboration but also enhances credibility with external stakeholders, including customers, investors, and regulatory bodies.
4. Empowering Employees:
Democratizing data empowers employees by equipping them with the knowledge and tools needed to perform their roles more effectively. It reduces dependency on centralized data teams or IT departments for routine data queries and analyses, enabling faster response times and more agile decision-making. Employees feel empowered and valued when they can access the data relevant to their responsibilities, enabling them to take ownership of their work and contribute proactively to organizational goals.
Strategies for Democratizing Data
1. User-Friendly Data Visualization Tools:
Investing in intuitive data visualization tools is essential for democratizing data. These tools enable users to explore complex datasets through interactive charts, graphs, and dashboards without requiring advanced technical skills. Platforms such as Tableau, Power BI, and Google Data Studio provide user-friendly interfaces that facilitate data exploration and interpretation, making insights accessible to a broader audience.
2. Data Literacy Training Programs:
Promoting data literacy across the organization is critical for successful data democratization. Data literacy training programs should focus on teaching employees how to interpret data, ask meaningful questions, and derive actionable insights. By improving data literacy skills, organizations empower employees to become more confident and proficient in using data to support decision-making and achieve strategic objectives.
3. Implementing Self-Service Analytics Platforms:
Self-service analytics platforms enable users to access and manipulate data independently, reducing reliance on specialized data teams or IT support. These platforms provide pre-defined datasets, templates, and tools that allow users to generate reports, conduct analyses, and visualize trends without requiring programming knowledge. Examples include platforms like Looker, Domo, and Qlik Sense, which empower users to explore data and gain insights autonomously.
4. Establishing Robust Data Governance Frameworks:
While democratizing data aims to increase accessibility, it is essential to maintain data integrity, security, and compliance. Establishing robust data governance frameworks ensures that data remains accurate, consistent, and secure throughout its lifecycle. Data governance involves defining clear policies, roles, and responsibilities for data management, as well as implementing measures to protect sensitive information and ensure regulatory compliance.
Data Analytics Tools that Can Help
1. Tableau:
Tableau is a powerful data visualization tool that allows users to create interactive and shareable dashboards. It supports a wide range of data sources and provides intuitive drag-and-drop functionality for exploring and analyzing data.
2. Power BI:
Microsoft Power BI is a business analytics solution that enables users to visualize data and share insights across their organization or embed them in apps or websites. It integrates with other Microsoft products and supports real-time data analysis.
3. Google Data Studio:
Google Data Studio is a free data visualization tool that allows users to create interactive dashboards and reports. It connects seamlessly with Google Analytics, Google Ads, and other data sources, making it easy to visualize and share data insights.
4. Looker:
Looker is a data exploration and business intelligence platform that provides users with the ability to create and share reports, dashboards, and visualizations. It offers a modeling layer that simplifies complex SQL queries and allows for data exploration without deep technical knowledge.
5. Domo:
Domo is a cloud-based business intelligence platform that integrates with multiple data sources, allowing users to visualize and analyze data through interactive dashboards. It supports real-time data updates and collaboration features for sharing insights across teams.
6. Qlik Sense:
Qlik Sense is a self-service data visualization and analytics platform that enables users to create personalized, interactive data visualizations and reports. It offers associative data indexing, allowing users to explore data relationships and uncover insights dynamically.
Case Studies in Democratizing Data
1. Netflix:
Netflix has democratized data access through its platform called ‘Metaflow,’ which provides employees with centralized access to data and tools for conducting analyses and developing machine learning models. This approach enables teams across the organization to collaborate effectively on data-driven projects, leading to insights that drive content recommendations, user experience enhancements, and operational efficiencies.
2. Airbnb:
Airbnb utilizes a self-service analytics platform known as ‘Airpal,’ which allows employees to query and analyze data stored in its data warehouse independently. This platform empowers employees from various departments—including marketing, operations, and customer support—to explore data, identify trends, and make data-informed decisions to enhance customer experiences and optimize business processes.
3. Uber:
Uber leverages ‘Kepler.gl,’ a data visualization tool that enables employees to create custom maps and visualize geospatial data. This tool enhances data democratization by making complex location-based insights accessible to non-technical users across different teams, such as operations, logistics, and urban planning. By democratizing access to geospatial data, Uber improves decision-making and operational efficiency in managing its global transportation network.
Challenges and Considerations
1. Data Security and Privacy:
Democratizing data must be balanced with ensuring data security and privacy. Organizations must implement robust security measures, access controls, and encryption protocols to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access or breaches. Compliance with data protection regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, is essential to mitigate legal and reputational risks associated with data misuse or unauthorized disclosure.
2. Cultural and Organizational Resistance:
Some organizations may face cultural resistance to data democratization, particularly from teams accustomed to traditional hierarchical structures or concerned about sharing sensitive information. Addressing these challenges requires leadership buy-in, effective change management strategies, and ongoing communication to emphasize the benefits of democratizing data in driving organizational performance and innovation.
3. Data Quality Management:
Ensuring data accuracy, reliability, and consistency is crucial for effective decision-making and trust in data-driven insights. Organizations must invest in data quality management processes, including data validation, cleansing, and documentation, to maintain data integrity throughout its lifecycle. By establishing data quality standards and best practices, organizations can enhance the reliability of insights derived from democratized data and support informed decision-making.
Conclusion
Democratizing data is not merely about providing access to information; it’s about empowering individuals, fostering innovation, and driving organizational agility in a data-driven world. By breaking down silos, promoting data literacy, and implementing user-friendly tools and platforms, organizations can unlock the full potential of their data assets. As businesses navigate the complexities of digital transformation and competitive landscapes, democratizing data will continue to play a pivotal role in shaping a culture of innovation, transparency, and data-driven decision-making across all levels of the organization.
