Metadata-Driven Data Fabric: A Guide for the Future of Enterprise Data Management
Metadata-Driven Data Fabric: A Guide for the Future of Enterprise Data Management
In today’s data-driven world, organizations face the monumental task of managing vast amounts of information scattered across various sources, formats, and systems. This complexity not only complicates data accessibility and analysis but also hampers decision-making processes. To address these challenges, the concept of a “data fabric” has emerged as a strategic approach to streamline data management across diverse environments.
However, the true power of data fabric lies in its integration with metadata, which transforms it into a more dynamic and intelligent system capable of driving significant business insights and operational efficiency.
Brief Overview of Data Fabric
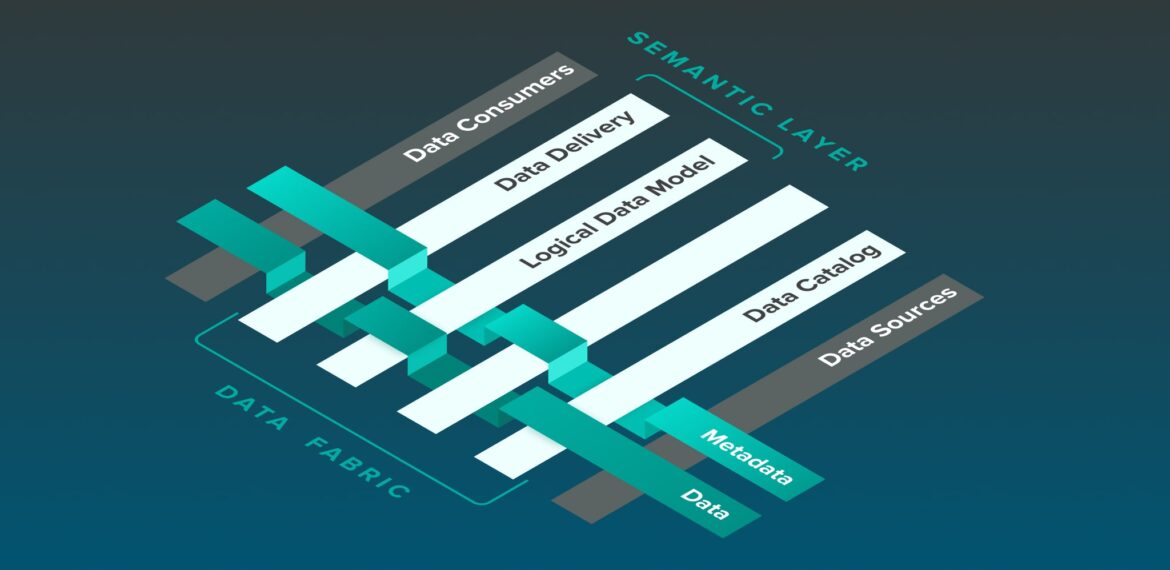
Data fabric is an architecture and set of data services that provide consistent capabilities across a choice of endpoints spanning hybrid multicloud environments. It is designed to simplify data management processes and make data readily available to users, irrespective of where it resides within the organizational ecosystem. By integrating data management tools and processes into a unified framework, data fabric allows for the automated and intelligent orchestration of data across platforms, from on-premises servers to cloud services.
Importance of Metadata in Modern Data Architectures
Metadata, often described as “data about data,” plays a crucial role in modern data architectures. It provides essential information about data elements, such as their structure, format, and usage, which is vital for effective data management and governance. In a metadata-driven approach, metadata acts as the backbone, enabling enhanced visibility, control, and automation across the entire data landscape. It helps organizations understand the lineage and quality of their data, comply with regulations, and derive actionable insights, making metadata indispensable in achieving high levels of operational intelligence and efficiency.
Understanding Metadata and Data Fabric
What is Metadata?
Metadata is essentially data that provides information about other data. It is crucial for understanding, using, and managing data effectively as it describes the basic characteristics of data, making it easier to locate and work with specific instances of data.
Types of Metadata
Metadata can be broadly classified into three main types:
Technical Metadata: This type of metadata deals with the design and specification of data structures, such as data types, formats, and schemas. It is used primarily by data engineers and IT professionals to ensure that the data ecosystem is correctly mapped and functioning as intended.
Operational Metadata: This involves data related to the operations performed on data, such as data lineage (the data’s origin and lifecycle), timestamp, and process information. It is crucial for managing data quality, auditing, and logging.
Business Metadata: This type provides context to data, making it useful for end-users and decision-makers. It includes information such as business terms and rules, ownership, and data sensitivity classification. Business metadata helps in data governance and compliance processes.
Examples of Metadata in Data Management
Data Lineage Information: Understanding where data comes from, how it moves through various processes, and how it is transformed.
Schemas and Database Catalogs: Definitions of database tables and columns that help in data organization and retrieval.
Data Quality Metrics: Information about data accuracy, completeness, and reliability, which supports effective decision-making.
Introduction to Data Fabric
A data fabric is an architecture and set of data services that provide consistent capabilities across a range of endpoints in a hybrid multicloud environment. It acts as an integrated layer that supports the global and efficient access, management, and processing of data throughout the organization.
Key Features and Components of Data Fabric
Integrated Data Management Tools: Unified interfaces for managing data across various platforms and locations.
Data Access and Delivery: Mechanisms that ensure data is consistently and securely accessible regardless of its physical location.
Automated Data Governance and Compliance: Tools that manage the metadata to ensure data meets regulatory compliance and internal standards.
How Data Fabric Simplifies Data Management Across Diverse Data Environments
Unified Data Environment: Provides a singular view of all organizational data, whether on-premises or in multiple clouds.
Enhanced Data Discovery and Access: Simplifies the discovery of data across the enterprise, reducing the time needed to gather and prepare data for analysis.
Automated and Intelligent Data Processes: Utilizes advanced analytics and machine learning to automate processes such as data quality checks, integration, and transformation, thereby reducing manual labor and improving accuracy.
Understanding both metadata and the data fabric provides a solid foundation for exploring how a metadata-driven approach can streamline operations and empower businesses with actionable insights. This comprehensive view is critical for harnessing the full potential of data assets in any modern organization.
The Role of Metadata in Data Fabric
Metadata is not just a supportive element in data management systems; it is a critical driver that enhances the functionality and efficiency of data fabrics. By understanding its role, businesses can better leverage their data fabric architecture to improve integration, accessibility, and governance.
Driving Integration and Accessibility
How Metadata Facilitates Seamless Integration of Various Data Sources
In complex data environments where data resides across multiple systems, metadata provides a common language and reference point that aids in the integration of these disparate data sources. By using metadata, data fabrics can automate the discovery and integration process, identifying relationships and dependencies between data from different systems.
For example, metadata descriptors can indicate that two different customer IDs in separate databases actually refer to the same entity, thus enabling a unified view of customer data across systems.
Metadata’s Role in Enhancing Data Accessibility and Usability
Metadata significantly enhances data accessibility by providing clear, understandable information about data attributes, such as data type, source, and last updated timestamps, which are crucial for users in locating and correctly utilizing the data. For instance, a data catalog enriched with metadata allows users to easily search for data across the enterprise by using familiar business terms.
Furthermore, metadata supports usability by providing context that can be critical for interpreting the data correctly, such as units of measurement or any caveats about data reliability.
Enabling Advanced Data Governance
Explanation of Metadata-Driven Governance Frameworks
Metadata-driven governance frameworks rely on metadata to enforce rules and policies that govern data usage across an organization. Such frameworks use metadata to automate many governance processes, including data quality monitoring, data lineage tracking, and compliance auditing.
For example, metadata can automatically flag data that does not comply with predefined quality standards or regulatory requirements for review or remediation.
Benefits of Using Metadata for Data Security, Quality, and Compliance
Data Security: Metadata can enhance data security by tagging sensitive or confidential data and enforcing security protocols based on these tags. Access controls, encryption, and other security measures can be dynamically applied based on metadata attributes.
Data Quality: By maintaining information on data origin, transformations, and validations, metadata helps ensure and improve the quality of data throughout its lifecycle. This leads to more reliable and accurate data for decision-making.
Compliance: Metadata supports compliance with various regulatory requirements by providing auditable records of data lineage, access, and processing activities. It ensures that data handling practices are transparent and compliant with laws such as GDPR, HIPAA, and others.
By enabling advanced data governance through metadata, organizations not only enhance operational efficiencies but also build trust in their data systems, ensuring that data-driven insights are both accurate and compliant with internal and external standards. This solidifies metadata’s role as a foundational element in the data fabric, pivotal for managing modern data challenges.
Implementing a Metadata-Driven Data Fabric
Implementing a metadata-driven data fabric involves careful consideration of the architecture and the integration of the right tools and technologies. This section provides insights into these aspects, helping organizations build an effective framework.
Architectural Considerations
Key Architectural Elements of a Metadata-Driven Data Fabric
Central Metadata Repository: This is the core component where all metadata is stored. It must be scalable and capable of integrating metadata from various sources. This repository serves as the central point of access for data management processes and governance.
Metadata Integration Layer: Essential for extracting and consolidating metadata from disparate systems, including databases, data lakes, and external data sources. This layer should support various metadata formats and protocols.
Metadata Management Tools: These tools should provide capabilities for metadata creation, maintenance, and dissemination. Features should include version control, change management, and metadata distribution to ensure consistency across the environment.
Data Cataloging and Discovery Tools: These tools use the metadata to provide a searchable repository of data assets. They help users discover, understand, and access data across the organization.
Governance and Security Framework: This should use metadata to enforce data governance policies, manage data access, and ensure compliance with data privacy and protection regulations.
Integration with Existing IT Infrastructure
Integrating a metadata-driven data fabric into existing IT infrastructure requires:
Compatibility with Legacy Systems: Ensure that the new architecture can connect with older systems and manage their metadata effectively.
Scalability and Flexibility: The architecture should scale as data volume and complexity grow and should adapt to technological advancements or changes in business strategy.
Minimal Disruption: Implementation should cause minimal disruption to ongoing operations. This may involve phased deployment or parallel running with legacy systems before full cutover.
Tools and Technologies
Overview of Tools and Technologies That Support Metadata Management Within a Data Fabric
Metadata Repositories: Solutions like Apache Atlas or Informatica’s Enterprise Data Catalog, provide robust environments for managing metadata.
Data Catalog Tools: Tools such as Cloudera and Qlik offer powerful search and discovery capabilities, enhancing the visibility and accessibility of data assets.
Data Integration Tools: Software like Talend and Apache NiFi, are crucial for integrating data and metadata from various sources into a unified system.
Challenges and Solutions
Implementing a metadata-driven data fabric can be a transformative endeavor for any organization, but it comes with its set of challenges. Understanding these obstacles and preparing with effective strategies can significantly enhance the chances of a successful implementation.
Common Challenges
Technical and Organizational Challenges in Implementing Metadata-Driven Data Fabric
Complex Integration Tasks: Integrating existing data systems with a new data fabric architecture often involves complex technical challenges, especially when dealing with legacy systems that might use outdated technologies or standards.
Scalability Issues: As data volumes grow, maintaining performance while scaling the metadata solutions can become challenging.
Data Silos: Breaking down data silos to create a unified data ecosystem requires not only technical solutions but also changes in departmental workflows and processes.
Organizational Resistance: Changes in technology, especially those that alter workflows or data access, can meet with resistance from users accustomed to old systems.
Impact of Data Quality and Metadata Quality
Poor quality of data or metadata can undermine the entire purpose of implementing a data fabric:
Data Quality: Inaccuracies, inconsistencies, and incompleteness in the data can lead to erroneous outputs and decisions.
Metadata Quality: If metadata is incorrect or incomplete, it can lead to mismanagement of data, such as improper integration, inefficiencies in data handling, and compliance risks.
Overcoming the Challenges
Strategies for Effective Metadata Management
Implement Robust Data Governance: Establish a strong governance framework that ensures continuous monitoring, quality control, and updating of both data and metadata. This includes setting clear policies and responsibilities for metadata management.
Use Automated Tools: Leverage automated tools for metadata generation, collection, and synchronization to reduce errors and administrative burdens.
Continuous Education and Training: Provide ongoing training and resources to help all users understand the importance and benefits of the metadata-driven approach, ensuring they can effectively use the new system.
Tips for Fostering Organizational Alignment and Culture Change
Engage Stakeholders Early: Include key stakeholders in the planning and implementation phases to align goals and expectations from the outset. Their input can also help tailor the solution to meet specific departmental needs.
Promote Transparency: Keep all processes transparent, particularly those related to how data is managed and used. This helps in building trust and acceptance among the workforce.
Highlight Benefits: Regularly communicate the benefits of the new system, such as improved efficiency, enhanced data quality, and better compliance. Success stories and case studies can be particularly persuasive.
Change Management Programs: Implement formal change management initiatives to help ease the transition. This should include comprehensive support and resources to address any concerns and challenges that users face.
By understanding and addressing these challenges head-on, organizations can smooth the path toward a successful implementation of a metadata-driven data fabric. These efforts not only mitigate the risks associated with such a significant transformation but also maximize the potential benefits, leading to a more data-centric and agile organization.
Future Trends and Predictions
As organizations continue to evolve in a data-driven landscape, the implementation of metadata-driven data fabric becomes a pivotal strategy in managing complex data ecosystems. This approach is set to redefine the future of data management, influenced by emerging technologies and evolving business needs. Here, we explore how these developments are likely to shape the trajectory of data fabric solutions.
How Metadata-Driven Data Fabric is Shaping the Future of Data Management
1. Enhanced Real-Time Data Operations: Metadata-driven data fabrics are enabling more dynamic data environments where decisions and insights are derived in real-time. With the expansion of IoT devices and real-time data streams, metadata can facilitate faster analysis and integration, providing businesses with the agility to respond to market changes instantly.
2. Increased Automation and AI Integration: As artificial intelligence and machine learning become more sophisticated, their integration into data fabric systems is expected to enhance the automation of data processes. Metadata serves as the guiding framework for AI algorithms to understand and act upon data, automating complex data management tasks such as data quality checks, lineage tracking, and predictive analytics.
3. Greater Emphasis on Data as a Service (DaaS): With metadata-rich data fabrics, organizations can better package and deliver data across different business units and even externally, streamlining the process of data sharing and collaboration. This approach will support the growing trend towards DaaS, where data is readily consumable by various stakeholders, promoting innovation and efficiency.
Emerging Technologies and Their Potential Impact on Data Fabric Solutions
1. Blockchain for Enhanced Security and Transparency: The adoption of blockchain technology in metadata-driven data fabrics can significantly enhance data security, governance, and compliance. Blockchain’s immutable ledger can provide a verifiable and auditable trail of metadata transactions, making it easier to manage data lineage and integrity.
2. Edge Computing for Improved Data Management at the Source: As edge computing continues to grow, integrating it with data fabric solutions will allow organizations to manage data closer to its source. Metadata will play a crucial role in ensuring that data handled at the edge adheres to the same governance and quality standards as data managed centrally.
3. Augmented and Virtual Reality (AR/VR): As AR and VR technologies mature, they could significantly benefit from metadata-driven data fabrics by providing contextual data that enhances user experiences. Metadata can help manage and deliver the vast amounts of data generated by AR/VR applications efficiently, enhancing performance and immersion.
4. Quantum Computing’s Impact on Data Processing Speeds: Although still in its nascent stages, quantum computing promises to revolutionize data processing speeds. For metadata-driven data fabrics, this means the ability to process and analyze metadata at unprecedented speeds, potentially reducing the time required for insights generation and decision-making.
As these technologies continue to evolve and integrate with metadata-driven data fabrics, businesses are likely to see a transformation in how data is managed, processed, and utilized. The future of data management looks promising, with metadata at the helm steering organizations towards more efficient, secure, and insightful data practices. This strategic integration not only supports current operational needs but also scales to meet future challenges and opportunities in the data landscape.
Conclusion
The implementation of a metadata-driven data fabric represents a significant step forward in the evolution of data management strategies. As we’ve explored, this approach is critical for enhancing data integration, accessibility, and governance across complex and disparate data landscapes. By centralizing metadata management, organizations can achieve a more cohesive understanding of their data assets, streamline their data processes, and ensure higher data quality and compliance with regulatory standards.
Moreover, the future of metadata-driven data fabrics is intertwined with the advancement of emerging technologies such as AI, blockchain, edge computing, and possibly quantum computing. These innovations promise to enhance the capabilities of data fabrics, making them even more efficient, secure, and scalable. The potential for real-time data operations, improved automation, and better data services positions metadata-driven data fabrics as a cornerstone of modern data architectures that are capable of supporting dynamic and increasingly data-driven business environments.
For businesses looking to remain competitive and agile in a rapidly changing digital world, investing in a metadata-driven data fabric is not just a technological upgrade; it’s a strategic necessity. It offers a sustainable advantage by empowering organizations with the ability to manage their data more effectively, make faster decisions, and leverage data-driven insights to drive business growth and innovation.
Is your business ready to harness the power of metadata-driven data fabric?
At Datahub Analytics, we specialize in implementing cutting-edge data fabric solutions that are tailored to meet your unique business needs. Whether you’re looking to improve data integration, enhance data governance, or drive innovation through advanced analytics, our team of experts is here to help. Don’t let data complexity hold your business back.
Contact us today to schedule a consultation and discover how our data fabric solutions can propel your organization into a new era of data-driven success.
