Synthetic Data Generation: Transforming Analytics with Artificial Datasets
Synthetic Data Generation: Transforming Analytics with Artificial Datasets
Did you know that over 90% of the world’s data has been generated in just the past two years? Yet, despite this explosion of information, organizations often struggle to access the quality, privacy-compliant, and diverse datasets they need to drive innovation and analytics.
As data becomes the cornerstone of decision-making, challenges like data scarcity, privacy regulations, and the sheer cost of acquiring and processing real-world data are holding businesses back. Enter synthetic data—a groundbreaking solution that mimics real-world data in structure and behavior while eliminating privacy risks and other constraints. By bridging the gap between demand and availability, synthetic data is reshaping the analytics landscape.
This blog explores how synthetic data generation is transforming the way businesses approach analytics. From its ability to bypass privacy barriers to its role in creating diverse, cost-effective datasets, synthetic data offers a new frontier for organizations looking to innovate and scale. Let’s dive into how this technology is revolutionizing analytics and unlocking untapped potential across industries.
The Growing Challenges of Real-World Data
Overview of Data Challenges
- Data Scarcity in Specific Domains
In many industries, the availability of high-quality data is severely limited. For instance, research on rare diseases often suffers from insufficient patient data, making it difficult to develop effective treatments. Similarly, niche industries struggle to gather the diverse datasets needed for meaningful insights, as the data pool is often too small or fragmented. - Privacy and Compliance Concerns
With increasing regulations like GDPR in Europe and HIPAA in healthcare, businesses face stringent requirements to protect sensitive data. The fear of breaches and fines discourages organizations from utilizing the full potential of their datasets, especially when dealing with customer or patient information. These regulations also complicate data sharing, further limiting opportunities for collaboration and innovation. - High Costs and Time Requirements
Collecting, cleaning, and maintaining real-world data is an expensive and time-consuming process. Teams must invest significant resources in ensuring data accuracy, addressing inconsistencies, and eliminating biases. For many organizations, these costs become a bottleneck, delaying projects and making data-driven decision-making less efficient.
Impact on Analytics
These challenges create a domino effect that hinders the ability of organizations to harness data for innovation, model training, and decision-making:
- Stalled Innovation: Without access to sufficient and diverse data, organizations struggle to experiment, test hypotheses, or build novel solutions. This stifles innovation and the ability to gain a competitive edge.
- Suboptimal Model Training: Machine learning models thrive on data diversity and volume. Limited or incomplete datasets result in poorly trained models that fail to generalize effectively, leading to biased or inaccurate predictions.
- Slow Decision-Making: Data scarcity and compliance hurdles delay insights, leaving businesses unable to respond quickly to market changes or customer demands. This lag in decision-making can have significant repercussions in fast-paced industries.
As these challenges grow, the need for alternative solutions like synthetic data becomes increasingly apparent. By addressing these pain points, synthetic data generation offers a way to overcome the barriers posed by real-world data.
What is Synthetic Data?
Definition and Explanation
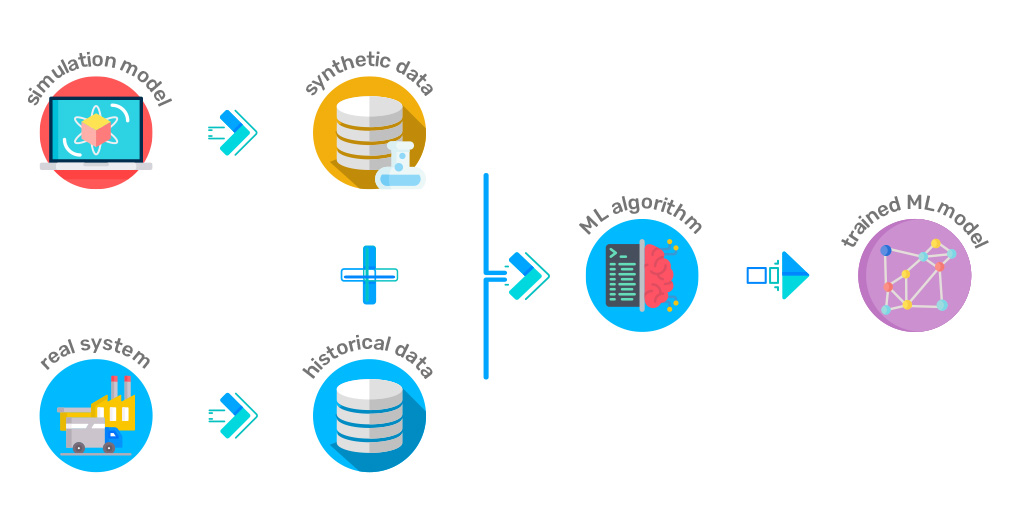
Synthetic data refers to artificially generated data that mimics the structure, characteristics, and statistical properties of real-world data without containing any actual real-world information. Unlike anonymized data, which is derived from real data, synthetic data is entirely created by algorithms and has no direct connection to original datasets.
The key distinction lies in its origin:
- Real-world data is collected through direct observations, transactions, or interactions.
- Synthetic data is generated programmatically to simulate real-world scenarios.
Synthetic data can be tailored to specific use cases, making it highly adaptable for applications where real data is scarce, sensitive, or expensive to obtain.
Types of Synthetic Data
- Structured Data:
- Tabular data commonly found in databases (e.g., customer information, financial records).
- Used in applications like predictive modeling, fraud detection, and CRM systems.
- Unstructured Data:
- Includes text, audio, and video data generated to mimic natural conversations or multimedia files.
- Applied in natural language processing, chatbot training, and media analytics.
- Image-Based Data:
- Synthetic images or videos designed for tasks like object detection, facial recognition, and autonomous driving.
- Example: Simulating traffic scenarios for self-driving car algorithms.
- Time-Series Data:
- Sequential data representing events over time, such as stock market trends or IoT sensor data.
- Crucial for applications in forecasting, anomaly detection, and process optimization.
How It’s Generated
Synthetic data is created using advanced technologies and algorithms that replicate the statistical patterns and relationships found in real-world datasets:
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs):
GANs use two neural networks—a generator and a discriminator—that work in tandem to produce realistic synthetic data. This approach is widely used for creating high-quality images, videos, and even text. - Statistical Modeling:
Statistical techniques generate synthetic data by simulating distributions, correlations, and other characteristics of real datasets. These methods are often used for tabular or time-series data. - Agent-Based Simulations:
Simulations involve creating synthetic environments where agents (e.g., virtual customers or vehicles) interact based on predefined rules. These interactions generate realistic datasets for various scenarios. - Programmatic Algorithms:
Rule-based programming and domain-specific logic create synthetic datasets tailored to specific needs, such as simulated financial transactions or healthcare data.
Synthetic data generation combines these techniques to provide datasets that are realistic, privacy-compliant, and ready to use, offering organizations a powerful tool to enhance analytics without the limitations of real-world data.
Benefits of Synthetic Data in Analytics
1. Enhanced Privacy and Compliance
Privacy concerns and stringent regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA make handling sensitive data a significant challenge. Synthetic data addresses these issues by ensuring that datasets contain no real-world personal or sensitive information while preserving their statistical integrity.
- Privacy Assurance: Because synthetic data is artificially created, it eliminates the risk of identifying individuals or exposing proprietary information. This makes it an ideal solution for industries like healthcare, finance, and education, where compliance is critical.
- Compliance-Friendly: Organizations can freely share synthetic data with partners or use it for research and development without the need for complex anonymization processes or legal clearances.
Example: A healthcare provider can generate synthetic patient records for AI model training, avoiding exposure of actual patient data while retaining valuable patterns such as demographics and medical histories.
2. Overcoming Data Limitations
Synthetic data is a powerful tool for filling gaps in datasets and addressing underrepresented scenarios. Real-world data may be insufficient, biased, or unavailable for specific use cases, limiting the effectiveness of analytics and machine learning models.
- Augmenting Datasets: Synthetic data can simulate rare events or niche scenarios, such as fraud detection, natural disasters, or rare disease modeling, ensuring comprehensive coverage in training datasets.
- Bias Reduction: By carefully crafting synthetic datasets, organizations can counteract biases inherent in real-world data, creating more equitable models and insights.
Example: A bank can generate synthetic transaction data to model unusual fraud patterns that might be too rare to capture in real datasets, enabling more robust fraud detection systems.
3. Cost and Time Efficiency
Traditional data collection and processing can be expensive, time-consuming, and logistically complex. Synthetic data eliminates these challenges by generating high-quality datasets programmatically.
- Reduced Collection Costs: Synthetic data bypasses the need for surveys, interviews, or expensive equipment, significantly lowering acquisition costs.
- Faster Time-to-Insights: With synthetic data, organizations can quickly generate datasets tailored to their needs, accelerating project timelines.
- Ease of Maintenance: Synthetic datasets are inherently clean and consistent, reducing the time spent on data preprocessing and validation.
Example: A retail company can generate synthetic customer purchase data to test a new recommendation engine without waiting for weeks of real-world transaction collection.
4. Improved Model Training
Machine learning models require diverse, high-quality datasets to perform effectively. Synthetic data enhances model training by providing customized datasets that address specific challenges.
- Diversity in Training Data: Synthetic data can simulate a wide range of scenarios, ensuring that models are exposed to varied inputs, improving their accuracy and robustness.
- Scalable Dataset Creation: Organizations can generate large volumes of synthetic data on demand, enabling models to handle big data tasks more efficiently.
- Testing Edge Cases: Synthetic data allows for simulating rare or dangerous scenarios, such as road accidents for autonomous vehicles or cybersecurity breaches for IT systems.
Example: An autonomous vehicle company can use synthetic data to simulate nighttime driving conditions, heavy rain, or complex traffic scenarios, which may be difficult to capture consistently in real-world datasets.
Synthetic data is rapidly becoming a game-changer in analytics, offering solutions to the limitations of real-world data. By ensuring privacy, addressing data gaps, cutting costs, and improving model training, synthetic data empowers organizations to innovate faster and more effectively.
Real-World Applications of Synthetic Data
1. Healthcare: Simulating Patient Data for Research Without Compromising Privacy
Synthetic data is revolutionizing healthcare by enabling researchers and organizations to work with patient-like data while fully safeguarding privacy.
- Use Cases:
- Simulating electronic health records (EHRs) to study treatment effectiveness.
- Creating data for rare disease research, where patient information is scarce.
- Training AI models for diagnostics without accessing real patient data.
Example: A hospital can use synthetic data to train a machine learning model for predicting disease outbreaks, ensuring compliance with HIPAA regulations while leveraging realistic datasets.
2. Finance: Creating Transaction Data for Fraud Detection Model Training
The financial industry requires extensive datasets to identify and prevent fraudulent activities, but real transaction data often contains sensitive personal information. Synthetic data provides a secure alternative.
- Use Cases:
- Generating diverse transaction patterns for fraud detection models.
- Simulating customer behavior to test credit scoring algorithms.
- Stress-testing systems with high-frequency trading data.
Example: A bank can generate synthetic credit card transaction data to simulate unusual spending patterns, enabling their fraud detection algorithms to recognize emerging threats.
3. Retail: Generating Customer Profiles for Personalization Models
Retail businesses rely on customer data to deliver personalized experiences, but privacy concerns and data limitations can hinder these efforts. Synthetic data solves these challenges.
- Use Cases:
- Creating synthetic customer profiles to train recommendation engines.
- Simulating purchase behavior to optimize inventory management.
- Developing marketing strategies using realistic consumer trends.
Example: An e-commerce platform can use synthetic customer data to refine its product recommendation system without accessing actual customer purchase histories.
4. Autonomous Vehicles: Producing Diverse Scenarios for Training Computer Vision Systems
Synthetic data is a cornerstone for training autonomous vehicles, where real-world data collection can be risky, expensive, and incomplete.
- Use Cases:
- Simulating various driving conditions, such as fog, rain, or nighttime scenarios.
- Generating diverse traffic situations to train computer vision systems.
- Testing edge cases like pedestrian crossings or sudden obstacles.
Example: A self-driving car company can use synthetic data to train its algorithms on rare but critical scenarios, such as a child running onto the road, ensuring the vehicle responds effectively.
5. Cybersecurity: Crafting Simulated Cyberattack Data to Improve Defense Mechanisms
Synthetic data helps cybersecurity teams prepare for and respond to emerging threats by simulating complex attack scenarios.
- Use Cases:
- Generating synthetic network traffic to detect anomalies.
- Simulating phishing attacks for employee training.
- Testing the resilience of IT systems against synthetic ransomware or DDoS attacks.
Example: A cybersecurity firm can create synthetic datasets to train AI models that identify malware signatures, improving detection rates without relying on sensitive or outdated real-world data.
These real-world applications demonstrate the transformative potential of synthetic data across industries. By enabling innovation while addressing privacy, cost, and data scarcity challenges, synthetic data is paving the way for more efficient, effective, and secure analytics solutions.
Challenges and Limitations of Synthetic Data
1. Authenticity Concerns
Synthetic data must closely mimic the statistical properties and patterns of real-world data to be effective. Poorly generated synthetic data can diverge from these patterns, leading to inaccuracies and unreliable insights.
- Key Issues:
- Over-Simplification: Simplistic generation methods may fail to capture the complexity of real-world datasets, resulting in oversimplified models that don’t perform well in real-world scenarios.
- Loss of Nuance: Subtle correlations or anomalies in real-world data may not be replicated in synthetic data, leading to blind spots in analytics.
Example: In a healthcare application, synthetic patient data that fails to accurately reflect comorbidities could lead to misleading outcomes in predictive modeling for treatment planning.
2. Bias Amplification
Synthetic data often relies on real-world datasets as a foundation. If the source data contains biases, these biases can be unintentionally amplified during the synthetic data generation process.
- Key Issues:
- Reinforcement of Existing Biases: Synthetic data can replicate and even exaggerate the demographic, behavioral, or systemic biases present in the original data.
- Introduction of New Biases: Flaws in generation algorithms or modeling assumptions may introduce biases that weren’t present in the real-world dataset.
Example: A hiring algorithm trained on synthetic data generated from a biased recruitment dataset could perpetuate discriminatory practices, such as favoring certain genders or ethnic groups.
3. Validation and Adoption
Despite its potential, synthetic data faces skepticism and challenges when it comes to validation and widespread adoption across industries.
- Key Issues:
- Validation Complexity: Verifying that synthetic data accurately replicates real-world data properties is a non-trivial task, requiring robust statistical and domain-specific validation techniques.
- Industry Hesitation: Many industries, especially highly regulated ones like healthcare and finance, are cautious about relying on synthetic data for critical decision-making due to concerns about authenticity and regulatory compliance.
- Trust in Performance: Organizations may hesitate to replace or supplement real-world data with synthetic data, fearing reduced accuracy or unforeseen issues.
Example: Financial institutions may be reluctant to use synthetic transaction data for fraud detection, as regulatory bodies might question the validity of models trained on non-real datasets.
Addressing the Challenges
To overcome these limitations, organizations need to focus on:
- Advanced Generation Techniques: Using cutting-edge tools like GANs and deep learning to improve the realism and diversity of synthetic data.
- Bias Mitigation Strategies: Implementing rigorous bias checks and using diverse source datasets to minimize bias in synthetic data.
- Robust Validation Frameworks: Developing industry-specific validation protocols to ensure synthetic data meets the required accuracy and reliability standards.
- Education and Advocacy: Raising awareness about the benefits and limitations of synthetic data to build trust and drive adoption.
While synthetic data holds immense promise, addressing these challenges is critical to fully realizing its transformative potential in analytics and decision-making.
The Future of Synthetic Data Generation
1. Technological Advancements
Emerging technologies are set to revolutionize synthetic data generation, enabling even greater realism, scalability, and efficiency.
- Advanced AI Models:
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) are becoming more sophisticated, producing hyper-realistic synthetic datasets for diverse applications, from medical imaging to autonomous vehicles.
- Foundation models, such as large language models, are being adapted to generate synthetic text, audio, and video data at unprecedented scales and levels of complexity.
- Quantum Computing:
- Quantum algorithms hold the potential to accelerate synthetic data generation by solving complex optimization problems faster than classical methods. This could enhance the realism and scalability of datasets, especially for large-scale simulations in industries like finance or logistics.
- Integration with Digital Twins:
- Synthetic data generation is increasingly being paired with digital twin technology to simulate real-world systems and environments. This combination offers unparalleled accuracy for predictive modeling and scenario testing.
Future Outlook: These advancements will enable businesses to create synthetic data that not only mirrors real-world patterns but also incorporates edge cases and dynamic variations, further enhancing its applicability.
2. Increased Adoption
As industries become more data-driven, the adoption of synthetic data is expected to expand rapidly.
- AI and Machine Learning:
- Synthetic data will become a cornerstone for training AI models, especially in areas where real data is insufficient, sensitive, or expensive to obtain. Industries like healthcare, autonomous driving, and natural language processing are already leading the way.
- Personalization and Marketing:
- Retail and advertising will increasingly rely on synthetic customer profiles to refine personalization strategies while adhering to privacy regulations.
- Global Collaboration:
- Synthetic data enables organizations to share datasets across borders and collaborate globally without breaching privacy laws, making it a vital tool for multinational companies.
Prediction: By 2030, synthetic data is expected to underpin a majority of AI and analytics projects, driving innovation in both established and emerging sectors.
3. Regulatory Impact
Synthetic data has the potential to reshape data privacy and sharing regulations by providing a privacy-preserving alternative to real-world data.
- Compliance Simplification:
- Regulatory frameworks like GDPR and HIPAA could evolve to explicitly endorse synthetic data as a compliant alternative for analytics, research, and model training.
- Data Sharing Enablement:
- Synthetic data may become a standard solution for enabling data sharing between organizations without the need for anonymization or de-identification processes.
- Regulatory Challenges:
- As synthetic data adoption grows, regulators may develop guidelines for its validation and use, ensuring that synthetic datasets meet accuracy and fairness standards.
Future Outlook: Governments and regulatory bodies will likely play a pivotal role in establishing best practices for synthetic data, fostering its adoption while ensuring ethical and transparent usage.
How to Leverage Synthetic Data for Your Business
1. Getting Started
Assessing your organization’s synthetic data needs and identifying use cases are crucial first steps. Here’s how to begin:
- Identify Data Challenges:
- Determine if your organization faces issues like data scarcity, privacy concerns, or high costs of real-world data collection.
- Consider industries or departments where data constraints are slowing down innovation (e.g., R&D, machine learning, or compliance-heavy sectors).
- Pinpoint Use Cases:
- Analyze specific scenarios where synthetic data could add value:
- Training machine learning models for niche or sensitive applications.
- Simulating rare or edge-case events for testing.
- Enabling privacy-compliant data sharing for partnerships or collaborations.
- Analyze specific scenarios where synthetic data could add value:
- Evaluate Feasibility:
- Review whether synthetic data can provide the necessary quality and realism for your intended applications.
- Consult domain experts to understand the intricacies of your data requirements.
2. Partnering with Experts
Engaging synthetic data generation providers or leveraging advanced tools can streamline the process and ensure high-quality outcomes.
- Choose the Right Providers:
- Look for vendors with proven expertise in synthetic data generation for your industry. Evaluate their tools for flexibility, scalability, and accuracy.
- Ensure the provider incorporates state-of-the-art technologies like GANs, agent-based simulations, or statistical modeling.
- Leverage Specialized Tools:
- Explore open-source or commercial synthetic data generation platforms tailored to your needs:
- For structured data: Tools like MOSTLY AI or Gretel.ai.
- For unstructured data: Libraries supporting image and video generation (e.g., StyleGAN).
- For simulation-based needs: Platforms like Unity for autonomous systems or AnyLogic for logistics.
- Explore open-source or commercial synthetic data generation platforms tailored to your needs:
- Pilot Projects:
- Start with a small-scale pilot to test the effectiveness of synthetic data in your workflows. Use the insights gained to refine your approach before scaling.
3. Measuring Impact
To ensure synthetic data delivers value, establish clear metrics and monitor its performance against business goals.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):
- Model Performance Metrics:
- Accuracy, precision, recall, or F1-score improvements in machine learning models trained with synthetic data.
- Data Coverage:
- How well synthetic data addresses gaps or represents rare scenarios.
- Cost and Time Savings:
- Reduction in data acquisition, cleaning, or annotation costs and time.
- Compliance Metrics:
- Ability to meet regulatory requirements while using synthetic data in analytics workflows.
- User Adoption Rates:
- Monitor how well stakeholders integrate synthetic data into their processes and whether it meets their expectations.
- Model Performance Metrics:
- Feedback Loops:
- Continuously gather feedback from teams using synthetic data and refine datasets based on their input.
- Comparative Analysis:
- Compare results from synthetic data with those achieved using real-world data to assess its impact on analytics accuracy and decision-making.
Conclusion
Synthetic data is revolutionizing the way businesses approach analytics by addressing the limitations of real-world data. From ensuring privacy and compliance to overcoming data scarcity, reducing costs, and improving model performance, synthetic data is a game-changer for organizations across industries. It empowers businesses to innovate faster, train AI models more effectively, and simulate scenarios that were previously impossible to replicate, all while maintaining ethical and regulatory standards.
As the demand for data-driven insights grows, synthetic data offers a powerful solution to unlock new opportunities and drive success. If you’re ready to transform your analytics and overcome data challenges, explore how synthetic data solutions can fit your business needs. Partner with us to leverage cutting-edge synthetic data generation tools and strategies that align with your goals. Let’s take the next step in advancing your data-driven journey—contact us today to learn more!
